Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is an advanced medical procedure involving pure oxygen inhaling in a pressurized chamber. The therapy’s premise is saturating the body with oxygen, which can foster healing in various physiological processes. Exploring the underpinnings of oxygen therapy in a hyperbaric context is instrumental in comprehensively understanding this intriguing therapy. HBOT’s principles are not recent discoveries, but their application in modern medicine reveals promising avenues for treating various ailments, ranging from chronic wounds to severe infections.
The Role of Oxygen in Healing
Central to the therapy’s efficacy is the role of oxygen as an essential element for life and recovery. Employing pure oxygen in a pressurized setting amplifies its therapeutic potential. Oxygen’s role extends beyond its critical function in cellular respiration; it is a keystone in the body’s healing ability. With increased oxygen in the bloodstream, areas with poor circulation can receive the necessary boost for tissue regeneration. It is why oxygen is often referred to as nature’s healer—a statement backed by substantial research on its benefits, which you can learn more about through this external resource.
The Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Process
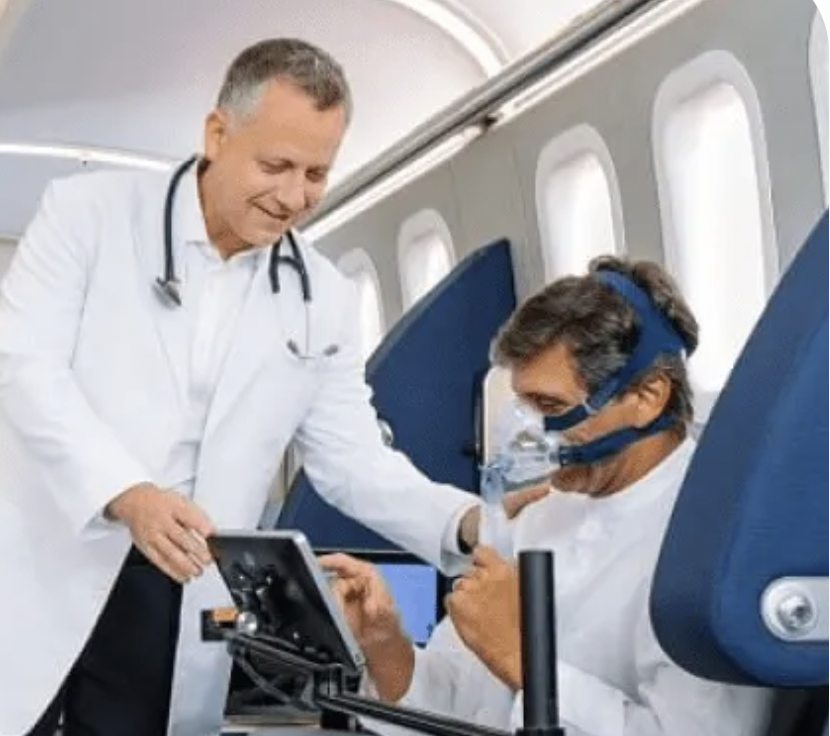
An HBOT session is quite distinct from other medical procedures. It involves the patient entering a specialized chamber capable of withstanding increased atmospheric pressure, often up to three times that of the everyday environment. Within this chamber, patients breathe in pure oxygen, which, due to the surrounding pressure, has a higher diffusion rate into bodily fluids, thus reaching areas that are usually less oxygenated. The condition being treated determines the length and frequency of these sessions, and a healthcare professional closely monitors the therapy to guarantee the best possible results.
Clinical Applications of Hyperbaric Therapy
The repertoire of HB OT’s medical applications is impressive and includes:
- Aiding the healing process of diabetes-related foot ulcers.
- Mitigating symptoms of decompression sickness experienced by divers.
- Treating severe bacterial infections like gangrene.
Furthermore, it has demonstrated beneficial effects in the realm of neuro-rehabilitation. Evidence suggests that with precise application, HBOT can facilitate recovery in a range of neurological conditions such as stroke and traumatic brain injuries.
Benefits of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Many clinical studies support HBOT’s advantages, which extend beyond accelerated healing. Improved infection control, enhanced neovascularization, and reduction in inflammation are among the listed benefits. Patients often report subjective improvements, such as increased clarity of thought and vitality, which can influence their life satisfaction and daily performance. These observed benefits underscore the potential for HBOT to serve as a complementary therapy in various treatment plans.
Understanding the Risks and Side Effects
Like all medical therapies, HBOT is associated with potential risks and side effects. Common side effects include ear pressure, similar to what one might experience during takeoff in an airplane, and mild sinus discomfort. More severe but rare complications like oxygen toxicity can occur and require immediate medical attention. Therefore, Patient selection is a critical component of HBOT protocols to mitigate such risks, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive medical evaluation before starting treatment.
Technology Advancements in Hyperbaric Therapy
In recent years, innovations in the design and functionality of hyperbaric chambers have materialized, making them more user-friendly and safer. Simultaneously, a concerted effort has been made to personalize HBOT protocols, leveraging data-driven approaches to calibrate oxygen levels and pressure to individual needs. Research on these advancements has been pivotal in expanding the applicability and efficiency of HBOT.
Hyperbaric Therapy in Sports and Athletics
The application of HBOT extends into the competitive sports arena, wherein athletes utilize the therapy for its perceived benefits of performance enhancement and expeditious injury recovery. The increased oxygenation is thought to reduce the recovery period required after intense physical exertion significantly or when recovering from sports-related injuries, which naturally aligns with the goals of competitive sports—to attain peak performance and rapid return to activity.
Insurance and Accessibility of Hyperbaric Therapy
Despite the treatment’s potential, the question of insurance coverage remains a hurdle for many individuals seeking HBOT. Coverage policies vary, often with strict criteria for qualifying conditions, underscoring a significant barrier to treatment access. For those not covered by insurance, the out-of-pocket cost can be prohibitive. It has led to discussions about the cost-effectiveness of the therapy and the necessity for healthcare systems to reevaluate their coverage criteria in light of emerging evidence regarding HBOT’s benefits.
The Future of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
The trajectory of HBOT research promises a fascinating future as scientists and clinicians explore its potential in previously untouched areas. There is particular enthusiasm about the role of hyperbaric therapy in augmented neuroplasticity, cognitive enhancement post-injury, and even as an adjunctive treatment in psychiatric conditions. These frontiers offer a glimpse into a future where HBOT could become a staple in diverse therapeutic regimens.
Final Thoughts
The dialogue surrounding Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy continues to expand as its scientific and therapeutic insights evolve. As we deepen our understanding of how oxygen under pressure can catalyze healing and rejuvenation, HBOT’s potential emerges more clearly. Balancing optimism with critical examination, we explore the vast landscape of this compelling therapy, seeking to validate its efficacy for a broader spectrum of conditions while prioritizing safety and patient-specific considerations.