The reliance of businesses and individuals on digital systems has catapulted the importance of cybersecurity. Every business, from small startups to multinational corporations, must face the numerous risks imposed by cyber threats if it maintains an online presence.
Moreover, cyber threats are constantly changing, making it necessary for any organizations and individuals to stay abreast of these developments. A cyber security guide would act as a basis for addressing such risks that are actually a cause for significant damage to organizations.
This article identifies some of the key risks a cybersecurity guide could alleviate by offering practical solutions towards ensuring the integrity and protection of sensitive information and digital assets.
1. Phishing Attacks
Phishing is one of the most common and successful cyberattacks. This has to do with how cybercriminals force people to yield passwords or credit-card details through deceptive emails, messages, or websites.
A cybersecurity guide could instruct its users on how to identify phishing attempts with guidance on confirming the legitimacy of messages before opening a link or providing sensitive information. With more complex phishing techniques such as spear phishing, there is a need for to-the-point guidance for individuals and organizations alike.
Most phishing attacks make use of human mistakes, so educating the users is a huge requirement too. A comprehensive cybersecurity guide can include sample copies of phishing emails, train the users on red flags to look out for, and instill a culture of skepticism around unsolicited communication.
2. Malware and Ransomware
One category of malware includes ransomware, where hackers encrypt the victim’s data and demand payment for the decryption key. Such attacks can result in significant loss, operational disruption, and reputational damage.
A cybersecurity guide will explain user understanding of the various types of malware, how they can be transmitted by malicious downloads, even as attachments within emails and infected USB drives. Such guides will also comment on the need for frequent updates of antivirus software and consistent backup of data to mitigate the extent of ransomware impacts.
This guide, by following best practices, will significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to malware.
3. Weak Passwords and Poor Authentication Measures
Hackers most commonly take advantage of weak passwords and poor authentication measures. There is always emphasis by the guides on cybersecurity on having strong unique passwords and multi-factor authentication to prevent intruders from accessing systems and data.
Simple passwords easily cracked through brute force attacks constitute one of the prime targets for cybercriminals.
For example, cybersecurity guides may train the user to create strong passwords and perhaps teach them how to manage these passwords with the help of password managers. Guides often require MFA implementation, requiring two or more authentication types-a password and a temporary code on a cell phone.
4. Internal Threats
While most risks to cybersecurity originate from external sources, the organization must also be prepared for internal risks. The personnel, vendors, or business associates with access to confidential data could adversely impact the data of a firm through actual intent or inadvertence.
The consequences of insider threats are sometimes the result of inadvertence, such as failure to follow security best practices, but are more often the result of bad intent, such as selling firm information or sabotaging systems.
Cybersecurity policies address all the risks highlighted above by outlining clear policies on the access and handling of data. The policies include training employees on cybersecurity best practice, ensuring that everyone in the organization is informed about their responsibility to the company’s data.
5. Data Breaches
Personal data, which may include Social Security numbers, financial records, and healthcare information, may be stolen and become ingredients for some identity theft or be sold on the black market. Data breaches bring hefty fines, loss of customer confidence, and potential lawsuits against businesses.
A cybersecurity guide offers protection against data breaches by providing them with strategies about promoting data encryption and good safe-data storage practices as well as regular system audits. Encryption ensures that if intercepted data is leaked, its content is not comprehensible to the unauthorized parties.
It indicates vulnerabilities in the defenses of an organization and ensures compliance with industry regulations. Therefore, by following these guidelines, businesses can keep their sensitive information safe from these assaults.
6. Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks attempt to flood a website, application, or network with traffic that exceeds the capacity of these resources. Denial of Service attacks may lead to massive periods of downtime that result in financial loss as well as damage to reputation and customer dissatisfaction.
This ultimate cybersecurity guide addresses strategies to mitigate DoS risk by establishing traffic filtering systems, CDNs, and monitoring network traffic for signs of abnormal activity. Last but not least, a good response plan is essential to minimize downtime and recovery time, especially in cases of an attack.
7. Social Engineering
These tactics that cybercriminals use to extract vital information from people or engage in acts that compromise security are called social engineering. It attacks through human psychology rather than technology.
A cybersecurity guide enlightens users to common attacks of social engineering; common tactics include pretexting, baiting, or impersonation. One will question requests for information or access whenever they seem suspicious. An organization can minimize the risk of successful social engineering attacks by developing a culture of security awareness and caution.
8. Risks in Cloud Security
Higher security stakes are associated with an increased migration of businesses to cloud operations. Such environments are prone to misconfigurations, access by unauthorized parties, and data leakage. With the vulnerabilities involved in such environments due to shared responsibility models between providers and customers.
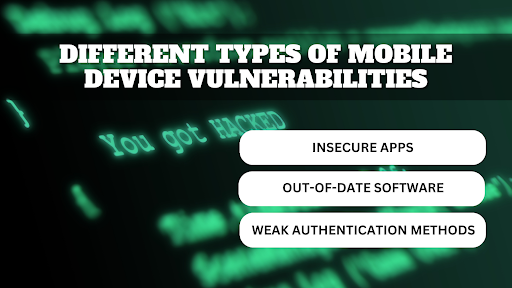
9. Mobile Device Vulnerabilities
The reasons for attacks on mobile devices are that cybercriminals love to target smartphones and tablets, leading to the very high deployment of these gadgets. Vulnerabilities such as insecure apps, out-of-date software, or weak authentication methods make a user a victim to various types of cyber threats such as malware or data theft.
A cybersecurity guide also keeps users’ mobile devices safe by advising them to update their software, not to download apps from unknown sources, and to have a strong password or biometric requirement. It can also be used in recommending MDM solutions that will lock down corporate data from employee devices while ensuring security policies are being followed.
10. Third-Party Risks
Other organizations depend on vendors for a myriad of services – from cloud storage to software development or payment processing. And such third parties introduce new vulnerabilities into an organization’s security system. A breach or compromise in a vendor’s systems creates a ripple effect at partner levels.
An appropriate guide in cybersecurity refers to the importance of vendor risk management and it does this by requiring organizations to vet their third-party vendors, thereby establishing security requirements.
It would also entail contractual responsibilities towards security practice and reassessment of the security posture of the vendor for continuous protection from potential threats.
Conclusion
By being constantly vigilant and informative, the threats against cybersecurity mean lessons every day.
Such a fully developed guide to cybersecurity is an important resource for everyone-from the individual to the organization emphasizing knowledge and strategies that have helped carry out significant risks such as phishing attacks, malware, insider threats, and cloud security vulnerabilities in order to ensure protection.
Implementing recommendations outlined in a good guide will keep the users well within the reach of cyberattacks, protect their sensitive information, and give them security assurance for their systems.
FAQs
- How can I protect myself from phishing attacks?
You can truly protect yourself from phishing attacks if you are cautious about unsolicited emails and messages and if the sender’s identity can be verified as well as not clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown attachments.
- What is multi-factor authentication, and why does this matter?
Multi-factor authentication is defined as an authentication that involves asking users to present two or more verification factors to gain access to an account or system. This provides an additional protection layer, making unauthorized access of the account difficult even when the compromised password is stolen.
- How often should I back up my data?
It would be wise to back up your data periodically, taking into consideration how quickly your data is changing. Critical business information should be backed up on a daily basis; personal users, conversely, should make sure they back up data at least once a week.